Abstract
Background. Some ADP ribosylation factors (ARF) and ADP ribosylation factor-like (ARL) family are involved in the regulation of certain cancers, but the role of ADP ribosylation factor-like 9 (ARL9) in gastric tumorigenesis remains elusive.
Objectives. The main aim of this study was to evaluate the ARL9 expression within stomach cancer cells and elucidate its influence on the modulation of cancer cell behavior.
Materials and methods. Differential ARL9 protein expression in normal stomach and stomach cancer tissue was ascertained through data sourced from the University of Alabama at Birmingham Cancer Data Analysis Portal (UALCAN). Quantitative analysis of ARL9 expression in gastric cancer tissue and its association with clinicopathological features was performed using quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) and western blot analysis (WB). Small interfering RNA (siRNA) was employed to suppress ARL9 protein expression in the human stomach gastric adenocarcinoma human gastric adenocarcinoma cells (AGS) cell line. Assessment of AGS gastric cancer (GC) cell proliferation, invasion and migration was performed using the 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide (MTT) and transwell techniques.
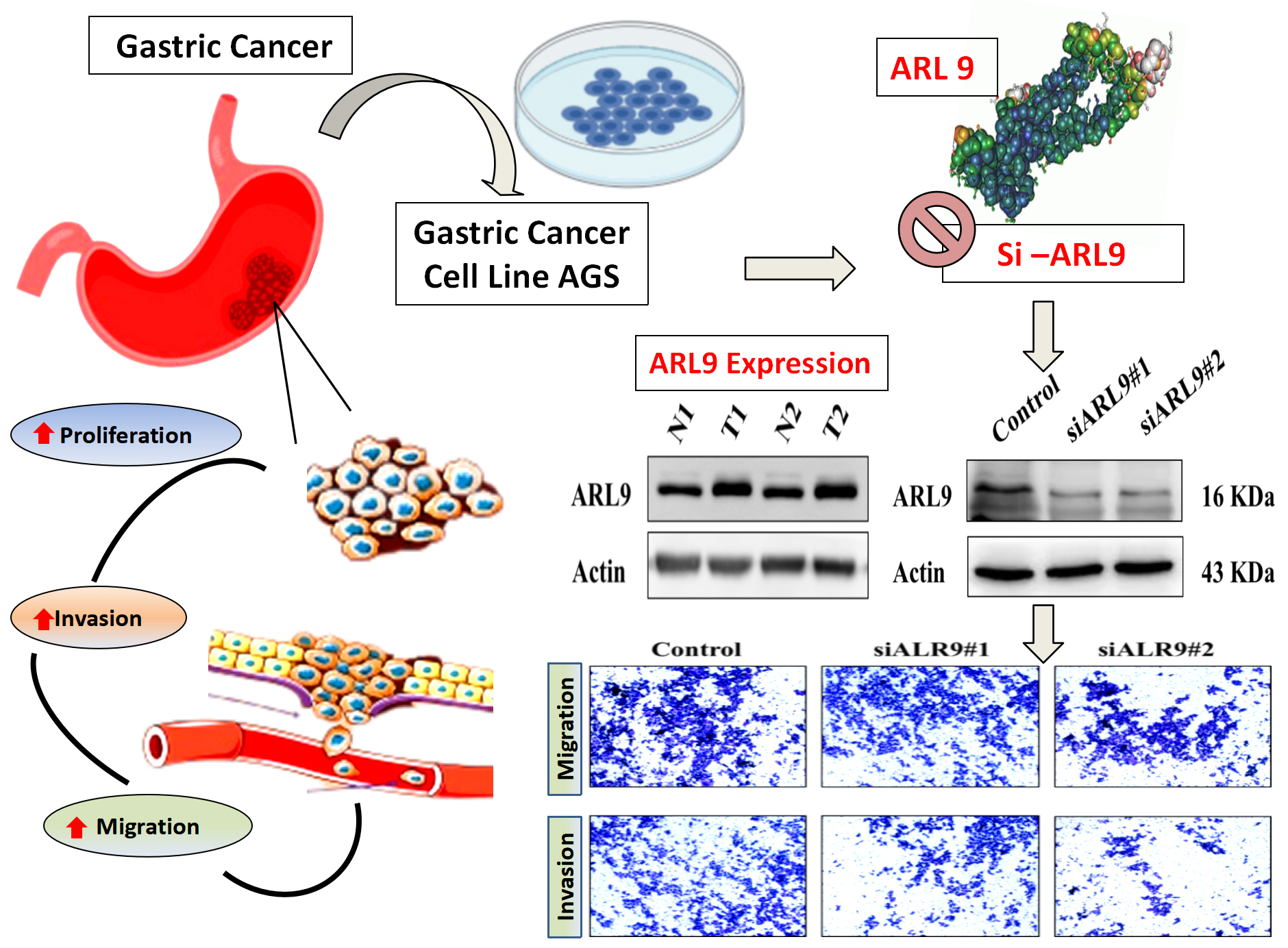
Results. The expression of ARL9 protein exhibited a significant upregulation in GC tissue, and showed a close association between tumor dimensions (p < 0.05) and the presence of distant metastases (p < 0.05) among individuals diagnosed with GC. However, no significant link was observed with sex, age and tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) staging in gastric malignancy patients. After the introduction of si-ARL9 in the experimental set, there was a noteworthy decrease in ARL9 protein levels in AGS cells (p < 0.01). In contrast to the control cohort, the restraint of ARL9 expression significantly hampered the growth, mobility and infiltration abilities of the AGS GC cell line (p < 0.01).
Conclusions. The significant correlation of ARL9 with the biological behavior of GC indicates its potentially pivotal role in the pathophysiology of the malignancy.
Key words: gastric carcinoma, ARL9, cellular growth, SiRNA intervention, metastatic dissemination
Background
Gastric cancer (GC) is a malignant disease influenced by a variety of factors, primarily environmental and genetic.1, 2 Recent statistical data places GC as the 4th most prevalent cancer worldwide, characterized by a median survival rate of less than 12 months.3 By 2023, the USA will have about 26,500 new cases of GC and about 11,130 deaths.4 Gastric cancer, known for its high invasiveness and heterogeneity, persists as a global health challenge.5 Notably, the majority of GC patients receive diagnoses at advanced stage, which often results in a poor prognosis. Simultaneously, the recurrence rate among GC patients remains elevated. Presently, the primary approach to treating GC involves surgical resection coupled with adjuvant chemotherapy or radiotherapy to attain curative outcomes.6 However, a substantial proportion of patients still experience recurrent GC within 5 years post-surgery, often with poor postoperative recovery.7 Consequently, it is essential to delve deeper into the molecular pathways responsible for the initiation and advancement of GC to discover innovative indicators for its diagnosis, prognosis and therapeutic objectives.
ADP ribosylation factor (ARF), a component of the RAS superfamily, has been confirmed to play a tumorigenic role in the development and spread of gliomas.8, 9 Previous reports highlight ARL2 and ARL3 as archetypal members within the ADP ribosylation factor-like (ARL) family, displaying reduced expression levels in gliomas. Research has revealed a negative association between the presence of these elements and the unfavorable survival outcomes and outlook for individuals with glioma.10, 11 Most importantly, ARF1 has been demonstrated to be upregulated in GC, which can be a novel prognostic marker for GC.12 In addition, ARLs are significantly dysregulated in GC and are involved in several cancer-related pathways. Among them, ARL4C is 1 of the 2 most significant clinical indicators for GC. Furthermore, ARL4C silencing remarkably inhibits the growth and metastasis of GC cells both in vitro and in vivo.13 Notably, ARL9, a newly recognized guanosine triphosphate (GTP)-binding protein, displays substantial preservation and broad distribution in eukaryotic organisms.14 Given its recent inclusion in the ARF family, the clinical significance of ARL9 protein in gastric tumorigenesis remains to be elucidated.
Objectives
The current study attempted to compare the expression of ARL9 between normal gastric tissue and GC tissue, in order to examine its relationship with clinicopathological parameters such as tumor growth and distant metastasis, and to investigate the effects of ARL9 silencing by siRNA transfection on proliferation, invasion and migration in human gastric adenocarcinoma cells (AGS) GC cells. The novelty of this study was to elucidate the role and regulatory mechanism of ARL9 in GC and to uncover a promising prognostic biomarker in GC patients. Another aim of the study was to enhance our understanding of the mechanisms underlying GC onset and progression, and identify potential therapeutic targets.
Materials and methods
Tissue samples
The RNA expression of ARL9 in GC tissues (n = 415) and normal stomach tissues (n = 34) was selected from The University of Alabama at Birmingham Cancer Data Analysis Portal (UALCAN) database (http://ualcan. path.uab.edu/index.html). The pathology department of Hengshui People’s Hospital (Hengshui, China) retained normal gastric tissue samples (n = 70), while clinical samples were collected from patients with GC who underwent surgical resection (n = 70).
Cell lines, chemicals and reagents
The AGS human GC cell line was obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC; Manassas, USA). Serum-free medium bovine serum and Roswell Park Memorial Institute-1640 (RPMI 1640) were purchased from Gibco (Waltham, USA). Immunohistochemistry utilized a universal EnVision two-step assay kit and diaminobenzidine (DAB) colorant acquired from Beijing Zhongshan Jinqiao Biotechnology Co. (Beijing, China). The rabbit anti-human ARL9 antibodies and mouse anti-human β-actin antibodies were purchased from Thermo Fisher Scientific (Waltham, USA). TransGen Biotech Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China) provided real-time fluorescence quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and RNA reverse transcription reagents. Six-well plates, transwell chambers, Lipofectamine 3000 transfection reagent, and TRIzol® reagent were acquired from Invitrogen (Waltham, USA). Throughout the experiment, the phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) served as a negative control. All cell experiments were performed in triplicate (n = 3).
UALCAN database
Using data from the UALCAN database, we analyzed RNA sequencing and clinical data from GC patients. The study involved examining ARL9 messenger RNA (mRNA) articulation in normal human stomach tissue, followed by statistical analysis and data visualization utilizing the information available in the record.
The inclusion and exclusion criteria
The inclusion criteria were as follows: 1) no age or sex bias; 2) patients undergoing surgical treatment; 3) a pathological diagnosis of GC; 4) complete survival information. The exclusion criteria were as follows: 1) multiple tumors in situ; 2) distant metastasis; 3) incomplete tumor staging; 4) incomplete information.
Immunohistochemistry
Sections of GC tissue were cut into continuous pieces about 4-μm thick, fixed in paraffin and stored with a 10% formalin. According to the experimental guidelines, Beijing Zhongshan Jinqiao Company’s universal EnVision two-step reagent kit and DAB kit were used to identify the expression of ARL9 protein in GC. Following that, the sections were divided into 3 groups according to the intensity of staining: cells with no staining received a score of 0; cells stained light yellow received a score of 1; and cells stained brownish yellow received a score of 2. Independent pathologists diagnosed every outcome.15
Cell culture
The human GC cell line AGS was kept alive in RPMI-1640 medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 1% penicillin-streptomycin. The cells were cultivated in a 37°C constant-temperature chamber with 5% CO2, and the cell culture media was changed about every 1–2 days. Cell passaging was done when the cells in the culture dish reached 80% confluence or full confluence.
Cell transfection
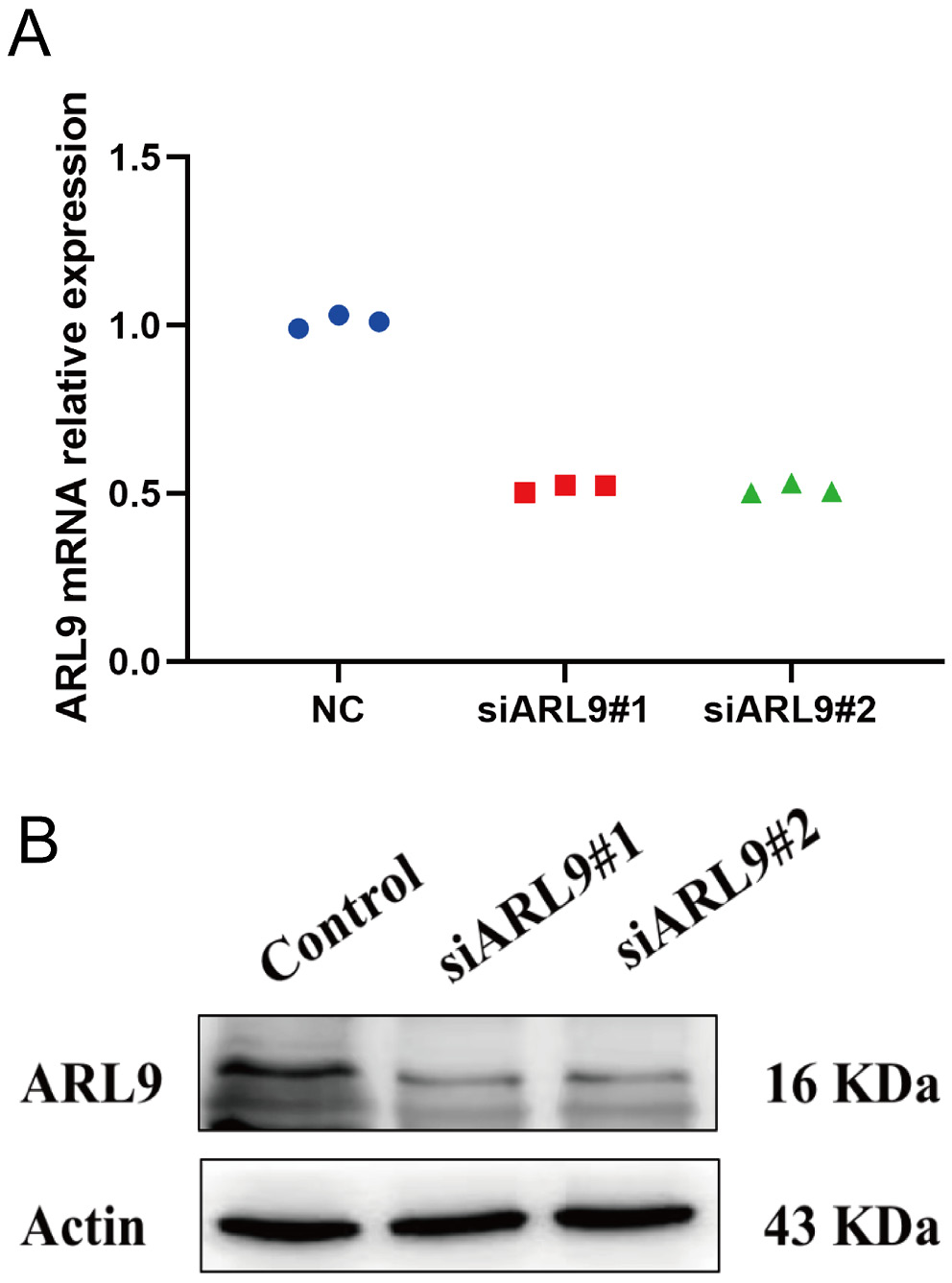
Approximately 1.5×105 cells per well were achieved by seeding and cultivating AGS cell lines in a 6-well plate until they reached the logarithmic growth phase. Following an overnight culture, the cell status was monitored. The Lipofectamine 3000 transfection reagent handbook was followed for transfection once the cell density reached 80%. Cells were transfected with the NC-siRNA in a control group and with si-ARL9 in an experimental group, respectively. Cells were harvested and total protein was extracted 48 h after transfection. The cell state and density were examined under a microscope (IM-3; OPTIKA, Bergamo, Italy), and the culture media were quickly changed. Western blot (WB) and quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) were then used to evaluate the effectiveness of transfection. For ARL9, Shanghai Jima Biological Company provided the negative control and the si-RNA sequences (si-ARL9-1 and si-ARL9-2). Transfection efficiency was assessed with WB and qPCR 48 h after transfection.16
MTT assay for assessing GC cell proliferation capability
After the well-cultured GC cell line AGS was subcultured and injected, 6 parallel control wells were placed in each group of a 96-well plate. After seeding each well with about 1×103 cells, the remaining wells received an equivalent volume of PBS solution. Prior to testing, 96-well plates were first aspirated of their culture media. After that, each well received 100 μL of 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide (MTT) mixture, which was made by dividing culture medium and MTT solution in a 1:9 ratio. Each well was then incubated for 1 h at 37°C. Then, 100 μL of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) solution was added and the mixture was discarded. The plate was stirred in the dark for 20 min. Finally, a microplate reader was used to measure and record the absorbance at optical density (OD) of 570 nm.17
Transwell assay for assessing the metastatic capability of GC cells
AGS, a well-cultured stomach cancer cell line, was counted and trypsinized. A serum-rich medium comprising 800 μL was put beneath every well. Above, a transwell chamber was placed, and 200 μL of serum-free media containing 6×104 stomach cancer cells were added. The chamber was then taken out of the setup and left in an incubator set at 37°C for 8 h. Following that, it was cleaned with a PBS solution, fixed for 1 h with a 90% ethanol solution, and then stained for 10 min with a crystal violet solution. Afterwards, a soft water stream was used to rinse the chamber, and a cotton swab was used to remove any leftover crystal violet solution from the edge of the chamber. Three randomly chosen visual fields from the microscope observation were chosen for statistical analysis and counting.17
Statistical analyses
Data analysis was conducted using IBM SPSS v. 22.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, USA) and R (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria) software. The Pearson’s χ2 test was performed on clinical and demographic characteristics of the patients. The Shapiro–Wilk normality test was conducted to confirm that the distribution was acceptable, and the normality of the distribution was not checked for a very large group (using the central limit theorem for n > 100). For the data with a non-normal distribution, the median of Q1–Q3 was used to represent the data. Comparisons between the 2 groups were conducted using the Mann–Whitney U test, and multiple groups were compared using Kruskal–Wallis tests followed by post hoc Dunn’s comparison tests. Non-parametric analysis of variance (ANOVA) test followed by Bonferroni post hoc test was chosen to analyze the proliferation ability. Pearson’s χ2 test of independence was used to test for a relationship between categorical variables. A p-value <0.05 was considered to be statistically significant. Main line of code from the WRS2 package for the nonparametric repeated measures ANOVA test into statistical analysis along with dedicated post hoc tests with Bonferroni correction is given below:
install.packages(“readxl”)
install.packages(“WRS2”)
library(readxl)
library(WRS2)
file_path<– “D:/data.xlsx”
data <– read_excel(file_path)
rm_anova_result<– aov(Score ~ Group * `Time Frame` * Replicate + Error(Group/`Time Frame`/Replicate), data = data)
summary(rm_anova_result)
kruskal_test_result<– kruskal.test(Score ~ Group, data = data)
print(kruskal_test_result)
wilcox_test_result<– pairwise.wilcox.test(data$Score,
data$Group, paired = TRUE, p.adjust.method = “bonferroni”)
print(wilcox_test_result)
Results
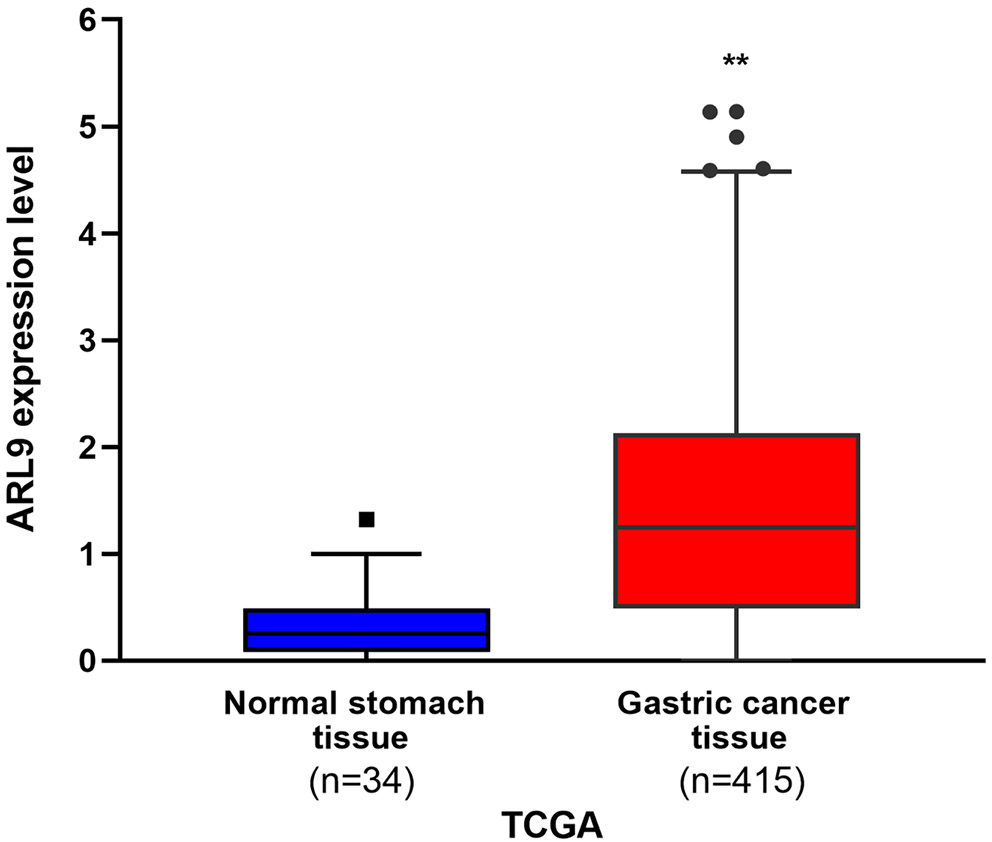
Analysis of ARL9 RNA and protein expression in normal gastric and GC tissues
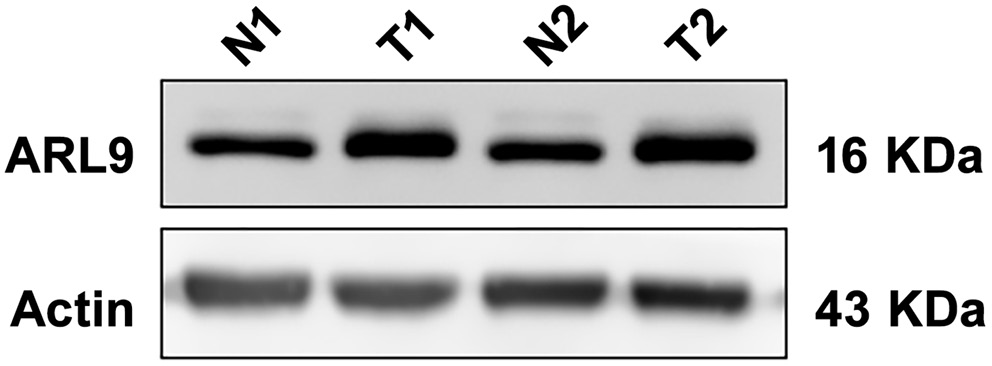
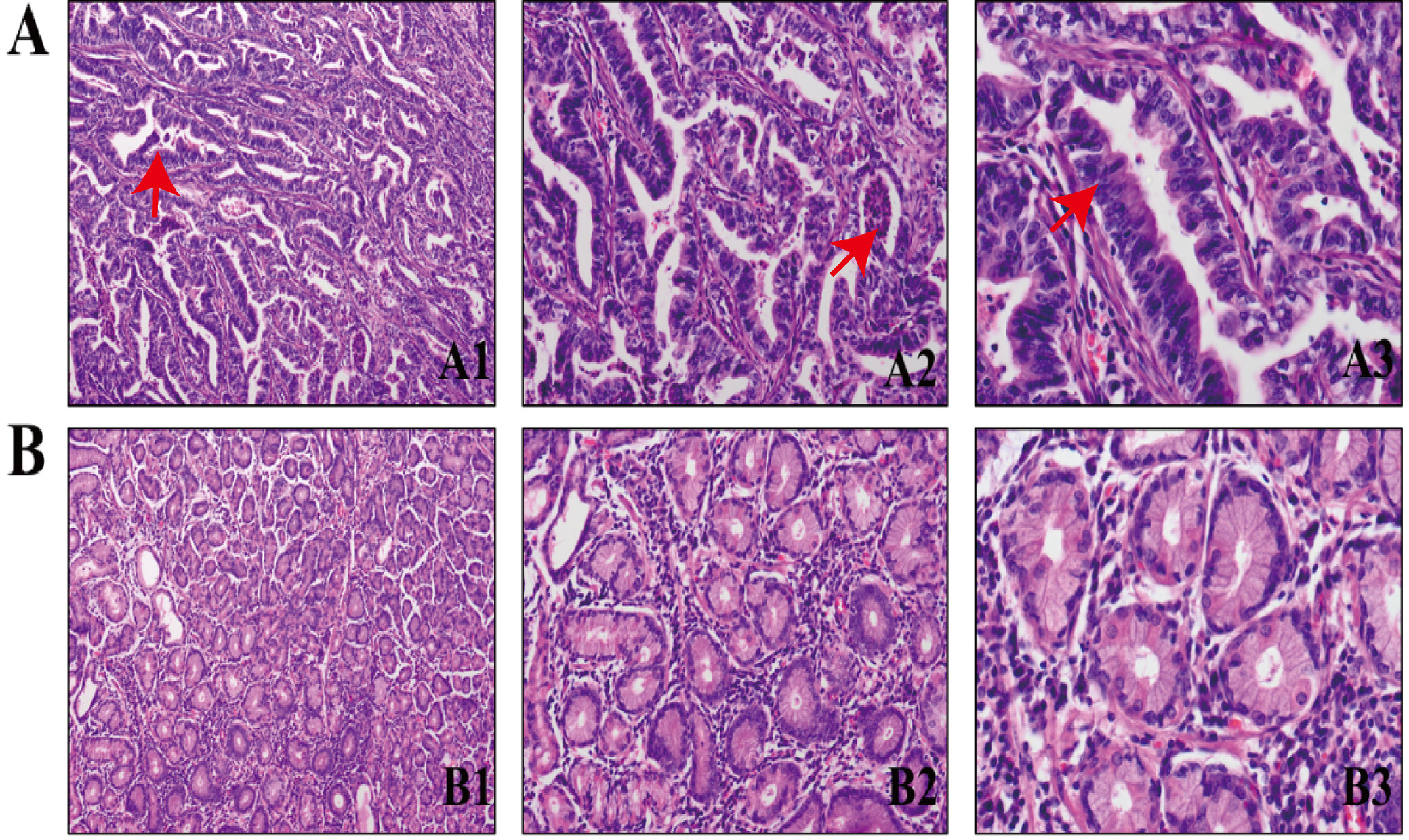
Using the UALCAN database, the RNA expression of ARL9 was examined in 415 GC tissues and 34 normal stomach tissues. Figure 1 shows that there was a significantly higher RNA expression of ARL9 in GC tissues (Mann–Whitney U test (U) = 11,861.50, Z-score = 6.61, p < 0.001; see Supplementary Table 1). Later, we used WB to evaluate ARL9 protein expression in 70 GC tissues and 70 normal gastric tissues that were taken from clinical samples. The data demonstrated that the ARL9 protein was upregulated in GC tissues but downregulated in normal gastric tissues (Figure 2). Five high-power visual fields were randomly selected for observation from each slice after immunohistochemical screening and evaluated semi-quantitatively.18, 19 The ARL9 protein expression differences between 70 GC tissues and 70 normal gastric tissues (degrees of freedom (df) = 1.00, χ2 =48.04, p < 0.001) were statistically significant. Conclusively, out of 70 normal gastric tissues, 15 showed positive expression, while in 70 GC tissues, 56 showed positive expression (expected frequency is presented in Supplementary Table 2). Additionally, human GC tissues and normal gastric tissues were validated with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining (Figure 3).
The correlation between ARL9 protein expression and clinical pathological parameters in GC tissue
A strong association was found between the results of 70 normal and GC tissues from each group and clinical case data. Regarding age, gender, tumor-mode-metastasis (TNM) stage, or lymph node metastases, we found no compelling associations. On the other hand, Table 1 shows a strong correlation (expected frequency is presented in Supplementary Table 3) between ARL9 protein expression and both distant metastasis (df = 1.00, p = 0.011) and tumor size (df = 1.00, χ2 = 11.50, p = 0.001).
Expression of ARL9 mRNA and protein in normal gastric and GC tissues
ARL9 expression in the GC cell line AGS was evaluated with reverse transcription qPCR (RT-qPCR), which measures ARL9 mRNA and protein levels after ARL9-specific NC, siARL9 #1 and siARL9 #2 are transfected. Figure 4A,B shows a decline in ARL9 mRNA and protein expression levels in the GC cell line AGS after transfection (df = 2.00, Kruskal–Wallis statistic = 5.45, p = 0.071, NC vs siARL9#1, p = 0.130; NC vs siARL9#2, p = 0.130, siARL9#1 vs siARL9#2; p = 0.999).
Assessment of proliferation and invasion capabilities of ARL9 in the GC cell line AGS
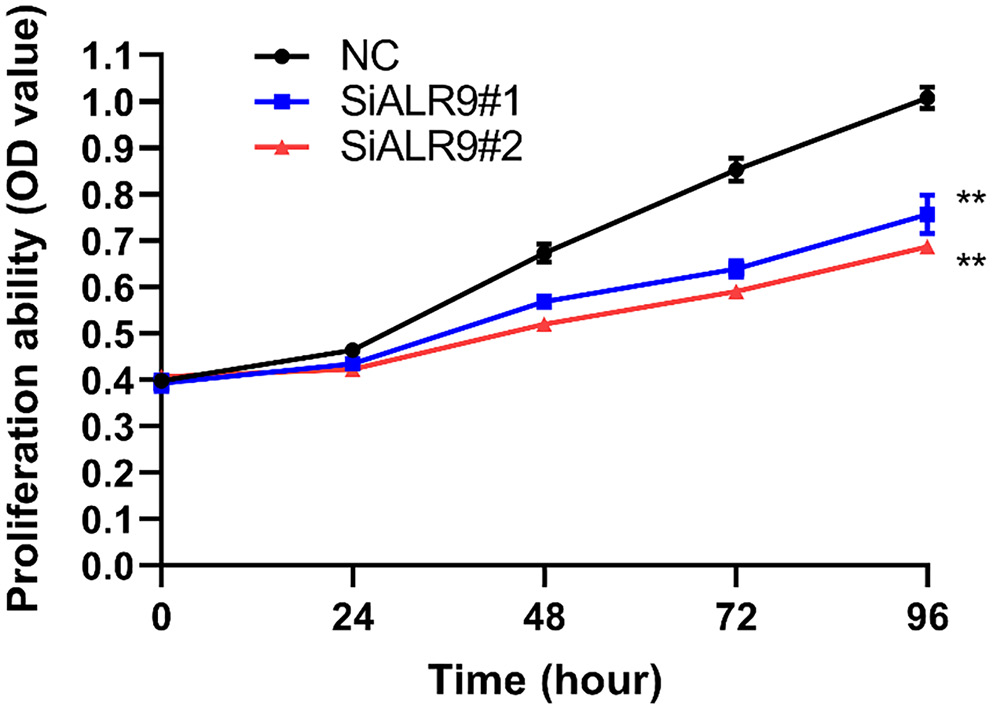
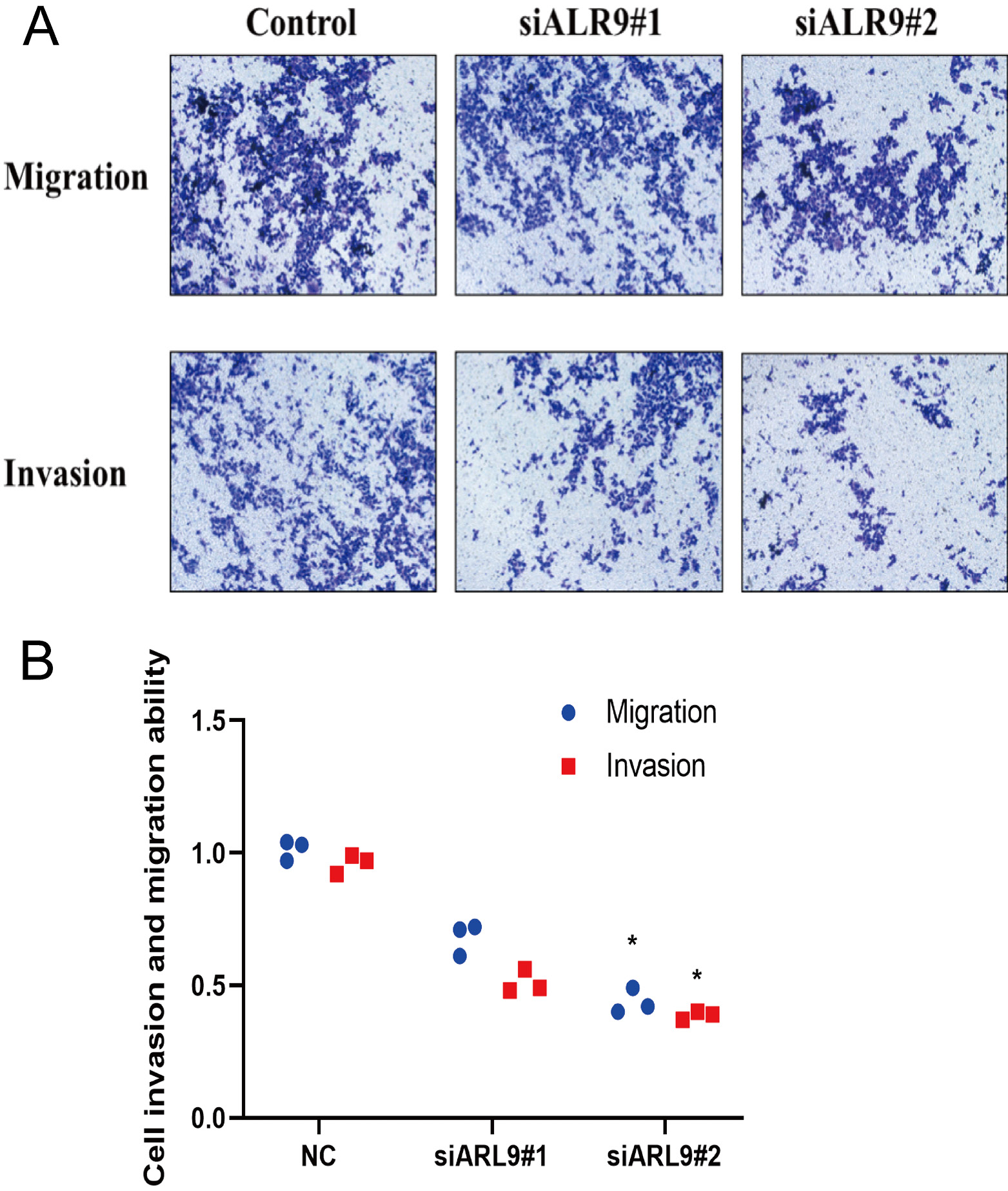
At time points of 0, 24, 48, 72, and 96 h following transfection, the MTT assay was utilized to assess the impact of ARL9 on the capacity of GC cells AGS to multiply. The results demonstrated a statistically significant difference between the NC group and the siARL9 #1 and siARL9 #2 transfected groups in terms of the AGS cells’ capacity to proliferate (Figure 5; df = 2.00, Kruskal–Wallis statistic = 3.37, p = 0.185; NC vs siARL9#1, p < 0.001; NC vs siARL9#2, p < 0.001, siARL9#1 vs siARL9#2, p = 0.013; Table 2). The effect of the protein on the invasive and migratory capabilities of AGS cells was evaluated 48 h after ARL9 transfection using cell counts and the transwell method. Microscopic studies revealed significantly decreased invasion and migratory potentials of AGS cells in the siARL9 #2 transfected groups compared to the NC group (Figure 6; for both invasion and migration: df = 2.00, Kruskal–Wallis statistic = 7.20, p = 0.027; NC vs siARL9#1, p = 0.539; NC vs siARL9#2, p = 0.022, siARL9#1 vs siARL9#2, p = 0.539).
Discussion
The precise mode of action and clinical significance of the ARL9 gene in tumors remains unclear, although analogous oncogenes have been identified and documented in previous research.20, 21 A negative association has been established between gliomas22 and the malignant growth of prostate tumors.14 Tumor suppressor protein ARF controls apoptosis, ageing and cell proliferation, all of which are vital in halting the growth of cancer.23 The fundamental function of ARF in inhibiting tumor growth has been thoroughly described. Its function as a suppressor of tumor growth is strongly associated with the p53 MDM2 axis, mostly because of its capacity to react to oncogenic cues like c-MYC and trigger p53 activation.24 The biological significance of ARL9, which is a recent member of the ARF family, in relation to tumors is still unknown.
In this research, we meticulously examined ARL9 expression using the public database UALCAN and subsequently corroborated our findings at both the protein and mRNA levels.25 In vitro experiments demonstrated a noteworthy downregulation of ARL9 protein and mRNA expression following ARL9 siRNA transfection. This reduction significantly impaired ce l proliferation and migration. Gastric cancer cells with elevated ARL9 protein expression exhibited greater proclivity for proliferation and metastasis than those with lower ARL9 expression.26 Additionally, ARL9 protein expression in GC tissues of patients with high ARL9 levels was confirmed by immunohistochemistry results to be highly associated with tumor growth and distant metastasis in patients with GC. However, p > 0.05 indicated no statistically significant correlation between TNM staging, age or gender of GC patients. Therefore, we draw the conclusion that the ARL9 protein is highly expressed in GC and may have the ability to promote the growth and migration of GC cells.
Limitations
Although our data suggest that ARL9 may play a role in the GC carcinogenesis, we must acknowledge that we have not thoroughly revealed the mechanisms of ARL9 protein in gastric tumorigenesis. This limitation highlights the need for further research to fully elucidate the role of ARL9 in GC, both in experimental settings and in complex molecular networks. In addition, a previous study re-ported that ARL9 was negatively regulated by ARL9 DNA methylation in low-grade glioma,22 so we should investigate the epigenetic regulatory mechanism of ARL9 expression in GC in future studies.
Conclusions
The study provides new insights into the ARL9 gene and sheds light on how it relates to gastric cancer.27 Given that ARL9 expression is downregulated in vitro after siRNA transfection and that this results in a decrease in cell migration and proliferation, it is highly probable that ARL9 is an oncogene in stomach cancer. These findings correlates with the previous research that demonstrated an inverse correlation between ARL9 and the development of malignancy in many cancer types.22, 28 For example,ARL9 as upregulated in colon adenocarcinoma and ARL9 silence reduced the proliferation and migration of colon adenocarcinoma cells.28 According to these data, ARL9 may be helpful as a diagnostic and prognostic marker for stomach cancer.
Supplementary data
The Supplementary materials are available at https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.13765995. The package includes the following files:
Supplementary Table 1. Statistical analysis for Figure 1.
Supplementary Table 2. Expected frequency for ARL9 protein expression.
Supplementary Table 3. Expected frequency for Table 1.
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.